Mastery the IDDSI Diet: A Comprehensive Guide to 0-7 Levels
Exploring the IDDSI Framework: From 0-7 Levels and Beyond in Dysphagia Diets
The IDDSI Diet: Simplifying Dysphagia Management When it comes to individuals with dysphagia or swallowing difficulties, managing their diet can be a complex and challenging task. That’s where the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) comes in.
The IDDSI diet framework provides a standardized and globally recognized system for classifying food and drink textures, making it easier for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and individuals with dysphagia to communicate and implement appropriate dietary recommendations.
The IDDSI diet framework aims to ensure safety and enhance the quality of life for those with dysphagia. It categorizes food textures and drink consistencies into standardized levels ranging from 0 to 7, allowing healthcare professionals to prescribe specific textures and consistencies based on individual needs and swallowing capabilities.
The Levels of the IDDSI diet
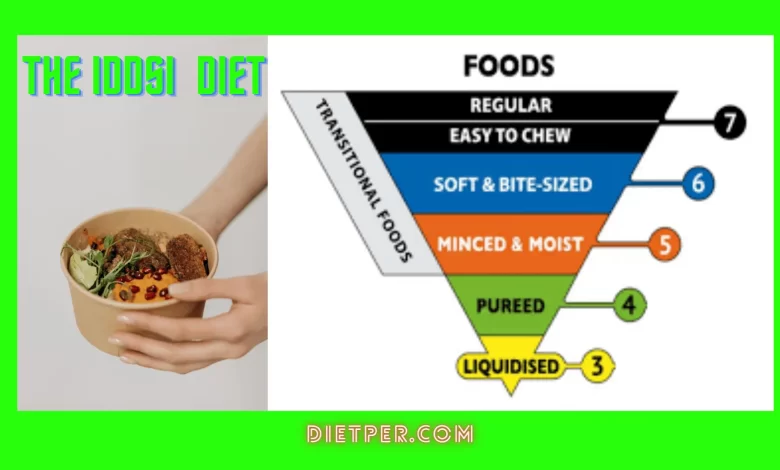
The heart of the IDDSI diet lies in its classification system, which categorizes both food and drinks into different levels of texture modification. Let’s take a closer look at these levels:
- Level 0: Thin liquids
- Level 1: Slightly thick liquids
- Level 2: Mildly thick liquids
- Level 3: Liquidised foods and moderately thick liquids
- Level 4: Pureed foods and extremely thick liquids
- Level 5: Minced and moist foods
- Level 6: Soft and bite-sized foods
- Level 7: Regular foods
8 Levels of The IDDSI Diet
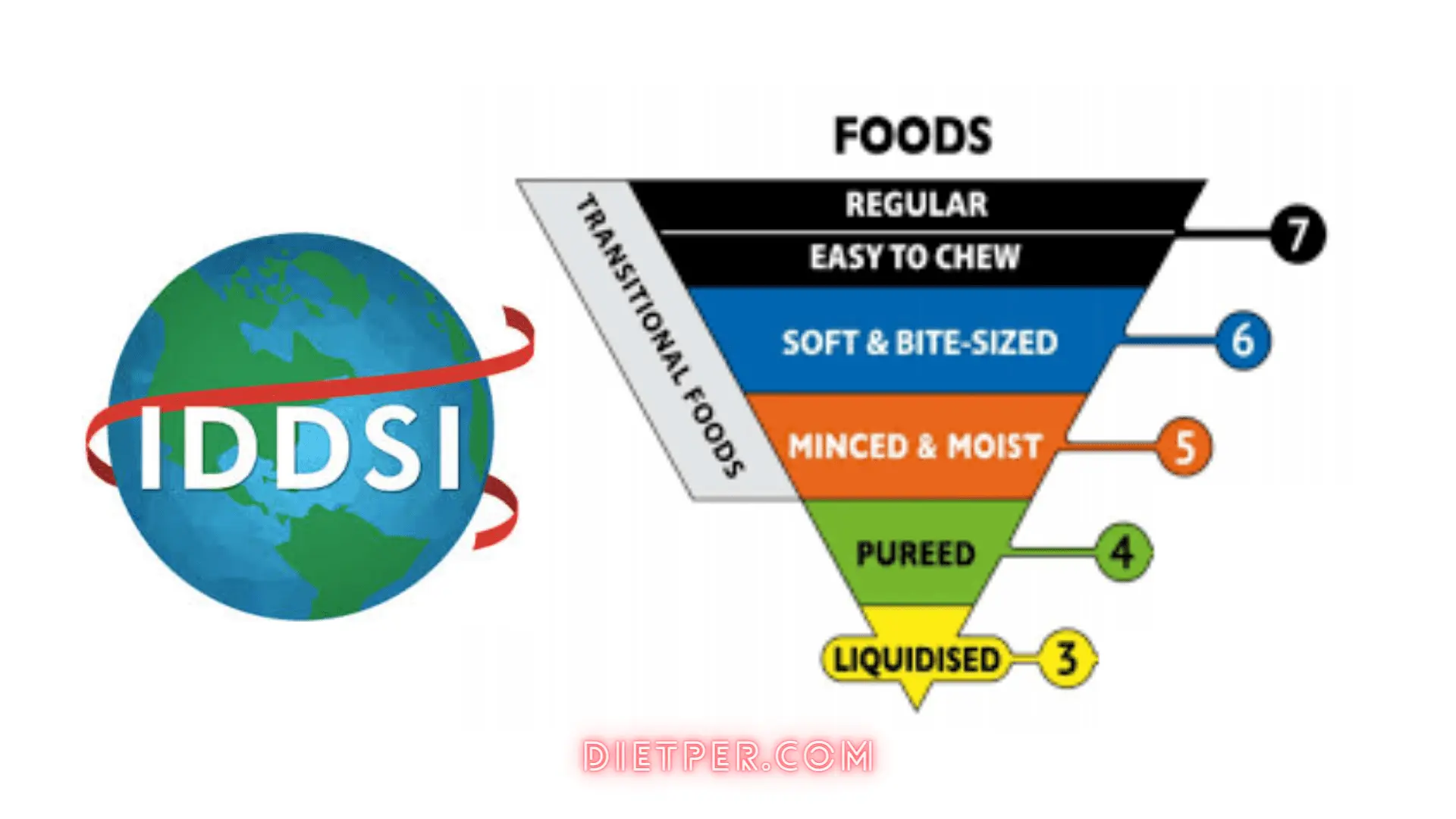
The IDDSI framework classifies food into eight levels (0-7), and beverages into three levels (0-4), each corresponding to a specific texture or thickness. Let’s explore these levels in more detail:
Level 0: Thin Liquids
Thin liquids are fluids that have a consistency similar to water. They are the least dense and require minimal effort to swallow. Examples include water, clear broth, and thin fruit juices.
Characteristics
- Fluidity: Thin liquids flow easily and quickly.
- Transparency: They are clear and see-through.
- No residue: After swallowing, there is no residue left in the mouth or throat.
Importance
- Level 0 liquids are essential for individuals with mild dysphagia or those who can safely manage thin consistencies. They provide hydration and are often the least restrictive in terms of dietary choices.
Level 1: Slightly Thick Liquids
Slightly thick liquids are thicker than thin liquids but still pourable. They have a slight resistance to flow and are often used to make liquids safer for individuals with mild to moderate dysphagia. Examples include nectar-like juices and honey-thickened liquids.
Characteristics
- Slight resistance: These liquids flow slower than thin liquids but are still pourable.
- Viscosity: They have a slightly thicker texture, similar to nectar.
- Transparency: They are usually clear or slightly cloudy.
Importance
- Level 1 liquids are important for individuals who have difficulty managing thin liquids due to dysphagia. They reduce the risk of aspiration while providing hydration.
Level 2: Mildly Thick Liquids
Mildly thick liquids have a thicker consistency than Level 1 liquids. They are often used for individuals with moderate dysphagia who require more viscosity to safely swallow liquids. Examples include yogurt-like drinks and mildly thickened soups.
Characteristics
- Moderate resistance: These liquids flow even slower than Level 1, requiring more effort to swallow.
- Viscosity: They have a consistency similar to yogurt or a smoothie.
- Opacity: They can be opaque due to added thickening agents.
Importance
- Level 2 liquids are crucial for individuals who are at risk of aspiration with thinner consistencies. They provide better safety during swallowing while still allowing for a variety of beverage options.
Level 3: Liquidized Foods and Moderately Thick Liquids
Level 3 includes both liquidized foods and moderately thick liquids. Liquidized foods are pureed to a smooth consistency, similar to baby food, while moderately thick liquids are thicker than Level 2 but still pourable. Examples include pureed vegetables, custards, and moderately thickened milkshakes.
Characteristics
- Liquidized foods: Smooth and pureed, with no solid particles.
- Moderately thick liquids: Thicker than Level 2 but still pourable, often resembling a thick milkshake.
- Versatility: Level 3 allows for a wide range of food and drink options.
Importance
- Level 3 is significant for individuals with severe dysphagia who cannot safely consume solid foods or thin liquids. It ensures that they receive both nutrition and hydration in a safe, swallowable form.
Level 4: Pureed Foods and Extremely Thick Liquids
Level 4 includes pureed foods and extremely thick liquids. Pureed foods are foods that have been blended to a smooth, homogenous consistency without any lumps or solid particles. Extremely thick liquids are liquids that are so thick that they don’t pour easily. Examples include baby food, mashed potatoes, and extremely thickened milkshakes.
Characteristics
- Pureed foods: Smooth, with no solid pieces or lumps.
- Extremely thick liquids: These liquids are very viscous and may require a spoon to consume.
Importance
- Level 4 is essential for individuals with severe dysphagia who cannot safely swallow any solid pieces or thin liquids. It provides them with nutrition and hydration in a form that minimizes the risk of choking or aspiration.
Level 5: Minced and Moist Foods
Level 5 consists of minced and moist foods. Minced foods are soft and finely chopped into small, manageable pieces. Moist foods are foods that are typically softer in texture and contain moisture. Examples include finely chopped cooked vegetables, moist meat, and mashed banana.
Characteristics
- Minced foods: Finely chopped into small, bite-sized pieces.
- Moist foods: These foods have a soft, tender texture and may contain natural moisture.
Importance
- Level 5 is suitable for individuals with moderate to severe dysphagia who can manage small, soft, and moist pieces of food. It provides them with options beyond pureed foods while reducing the risk of choking or aspiration.
Level 6: Soft and Bite-Sized Foods
Level 6 includes soft and bite-sized foods. These foods are soft, tender, and can be easily broken down with minimal chewing. They are typically cut into small, manageable pieces that can be bitten and swallowed safely. Examples include well-cooked pasta, soft fruits, and tender cooked vegetables.
Characteristics
- Soft texture: These foods are easy to chew and break down.
- Bite-sized pieces: The food is cut into small, manageable portions.
Importance
- Level 6 allows individuals with mild to moderate dysphagia to enjoy a wider variety of foods with more texture and flavor. It promotes a more satisfying dining experience while still ensuring safe swallowing.
Level 7: Regular Foods
Level 7 represents regular foods that do not require any modification. These are foods that most people without dysphagia can consume safely. Examples include whole fruits, bread, and unaltered meats.
Characteristics
- Unmodified: These foods are in their natural state and require regular chewing.
- Variety: Level 7 offers a wide range of food options.
Importance
- Level 7 is suitable for individuals who do not have swallowing difficulties. It allows them to enjoy a standard diet without the need for modifications, ensuring a diverse and satisfying culinary experience.
Some Popular Articles
- Unveiling: Top 9 Foods to Avoid While Intermittent Fasting
- 17 things to avoid during fasting and praying in Spiritual
- A Spiritual Feast: Foods to Eat While Fasting and Praying
The IDDSI Diet Framework
The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) is a globally recognized framework designed to standardize and improve the classification of food and drink textures for individuals with dysphagia, a swallowing disorder. The international dysphagia diet can affect people of all ages and is often associated with various medical conditions.
The IDDSI framework categorizes food and drink into a continuum of eight levels, ranging from Level 0 (thin liquids) to Level 7 (regular foods). Each level specifies the texture and thickness of food and drinks, making it easier for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and food service providers to select appropriate options for individuals with dysphagia. This framework enhances safety by reducing the risk of choking and aspiration pneumonia, which are common complications of dysphagia.
The IDDSI framework promotes clear communication among healthcare teams, patients, and caregivers, ensuring that everyone involved understands the specific dietary requirements. This standardization helps improve the overall quality of life for individuals with dysphagia by enabling them to enjoy a wider variety of foods and drinks while minimizing health risks.
Why the IDDSI Framework Matters?
The IDDSI framework is a game-changer in dysphagia management for several reasons:
- Clear Communication: It provides a common language for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and individuals with dysphagia, reducing confusion and ensuring consistent care.
- Safety: Categorizing textures reduces the risk of choking, aspiration pneumonia, and other complications associated with swallowing difficulties.
- Quality of Life: The framework allows individuals with dysphagia to enjoy a wider variety of foods and beverages, promoting a more satisfying dining experience.
- Global Impact: The IDDSI framework has gained international recognition, contributing to standardized dysphagia care worldwide.
The IDDSI liquids
The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) plays a crucial role in the management of dysphagia, a condition that affects an individual’s ability to swallow safely and effectively.
One of the key components of the IDDSI framework is the classification of liquids into various levels based on their thickness and consistency. This classification is of utmost importance as it helps ensure the safety and well-being of individuals with dysphagia by providing clear guidelines for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and food service providers.
- Level 0 – Thin (Water-like): At this level, liquids have a consistency similar to water. These are clear, unthickened fluids such as water, tea, and clear broths. Level 0 liquids are suitable for individuals with mild dysphagia who can manage thin fluids without the risk of aspiration.
- Level 1 – Slightly Thick: Liquids in this category are slightly thicker than water, with a “nectar-like” consistency. Examples include nectar-thick juices and some nutritional supplements. They are easier to control and less likely to lead to aspiration for those with moderate dysphagia.
- Level 2 – Mildly Thick: Mildly thick liquids are thicker than Level 1 and have a “honey-like” consistency. They include thickened juices, milkshakes, and some soups. Level 2 liquids are suitable for individuals with moderate to severe dysphagia who require more texture in their liquids.
- Level 3 – Moderately Thick: Liquids at this level have a consistency similar to pudding. They include foods like puddings, yogurt, and thickened cream-based soups. These liquids are typically recommended for individuals with severe dysphagia who need a highly controlled liquid texture.
- Level 4 – Extremely Thick: Level 4 liquids are extremely thick almost solid in consistency. They are served with a spoon and include foods like mousse, custard, or extremely thickened liquids used for hydration. These are for individuals with the most severe swallowing difficulties.
The IDDSI Training
The IDDSI (International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative) training is essential for healthcare professionals, caregivers, food service providers, and anyone involved in the care of individuals with dysphagia. This training is designed to educate and familiarize individuals with the IDDSI Diet framework, ensuring that they can accurately assess and provide appropriate food and drink textures for those with swallowing difficulties. Here are the key components of IDDSI training:
- Understanding Dysphagia
- IDDSI Framework
- Assessment and Evaluation
- Food and Drink Preparation
- Documentation and Communication
- Hands-On Practice
- Continuing Education
IDDSI training plays a critical role in enhancing the safety and quality of life for individuals with dysphagia. It ensures that healthcare providers and caregivers have the knowledge and skills necessary to provide appropriate texture-modified diets and liquids, reducing the risk of complications and improving the overall well-being of those with swallowing difficulties.
The IDDSI food
Ensuring safe and enjoyable meals for dysphagia patients is a top priority. The IDDSI Diet provides a standardized approach called the IDDSI Food Framework to enhance safety and communication. This framework classifies food and drink textures into eight levels, ensuring consistency and safety. For example, Level 3 is “liquidized/mixed,” and Level 6 is “soft and bite-sized.”
Implementing this framework requires collaboration among healthcare professionals, dietitians, chefs, and caregivers. Training and education are crucial for its effective use in various settings.
In conclusion, the IDDSI Food Framework is vital for individuals with dysphagia. It ensures safe and consistent meals, improving their quality of life and allowing them to dine with confidence and dignity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the IDDSI Diet?
The IDDSI diet refers to dietary guidelines and standards provided by the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) to classify food and drink textures for individuals with dysphagia, a swallowing disorder.
What is the IDDSI Level 6 Diet?
An IDDSI Level 6 diet consists of soft foods that can be easily mashed with minimal effort. These foods are typically served in bite-sized pieces and are suitable for individuals with mild dysphagia.
What is the Purpose of the IDDSI?
The purpose of the IDDSI is to standardize the classification of food and drink textures to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals with dysphagia. It aims to reduce the risk of choking and aspiration while allowing for a wider variety of enjoyable and nutritious meals.
What are the 4 Levels of the Dysphagia Diet?
The four main levels of the dysphagia diet are typically categorized as Level 1 (pureed), Level 2 (mechanically altered), Level 3 (soft), and Level 4 (regular). These levels represent different food textures suitable for individuals with varying degrees of swallowing difficulties.
What is a Dysphagia 7 Diet?
A Dysphagia 7 diet is not a standard term within the IDDSI framework. However, it may refer to regular, unmodified foods, as Level 7 in IDDSI represents foods that require no modification and are safe for individuals with no swallowing difficulties.
Conclusion – The IDDSI diet
The IDDSI diet framework enhances dysphagia management, providing standardized guidelines for food and drink textures. It improves the quality of life for individuals with swallowing difficulties, reducing choking risks and enhancing nutrition.
The IDDSI Diet ensures clear and consistent communication among healthcare professionals, caregivers, and patients. Moreover, it benefits healthcare facilities, food services, and manufacturers by promoting compliance, patient safety, and overall healthcare quality. Embracing IDDSI advances dysphagia care, making a positive impact on affected individuals and creating a safer, more inclusive dining experience.
Disclaimer
This blog post aims to empower you to make informed and health-conscious food choices. Your well-being is of paramount importance, and it’s essential to prioritize your health before embarking on any restrictive diets. Therefore, if you have any concerns, it is highly advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making dietary changes.




